置备机器
Pigsty 在节点上运行,这些节点可以是裸机或虚拟机。您可以手工置备它们,或使用 terraform 和 vagrant 这样的工具在云端或本地进行自动配置。
沙箱环境
Pigsty 带有一个演示沙箱,所谓沙箱,就是专门用来演示/测试的环境:IP地址和其他标识符都预先固定配置好,便于复现各种演示用例。
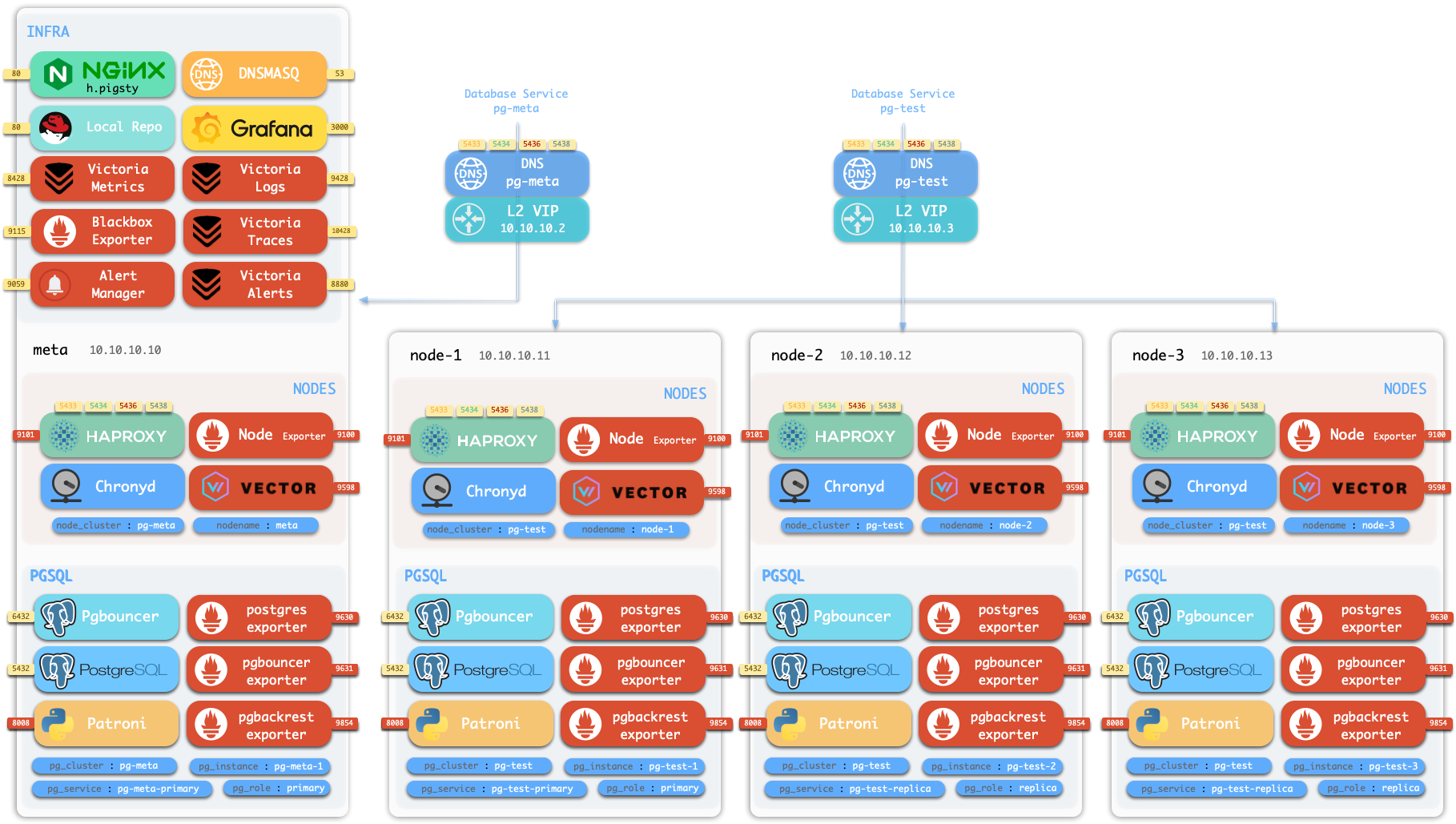
默认的沙箱环境由4个节点组成,配置文件请参考 full.yml。
沙箱的 4 个节点有着固定的 IP 地址:10.10.10.10、10.10.10.11、10.10.10.12、10.10.10.13。
沙箱带有一个位于 meta 节点上的单实例 PostgreSQL 集群:pg-meta:
meta 10.10.10.10 pg-meta pg-meta-1
沙箱中还有一个由三个实例组成的 PostgreSQL 高可用集群:pg-test,部署在另外三个节点上:
node-1 10.10.10.11 pg-test.pg-test-1node-2 10.10.10.12 pg-test.pg-test-2node-3 10.10.10.13 pg-test.pg-test-3
两个可选的 L2 VIP 分别绑定在 pg-meta 和 pg-test 集群的主实例上:
10.10.10.2 pg-meta10.10.10.3 pg-test
在 meta 节点上,还有一个单实例的 etcd “集群”和一个单实例的 minio “集群”。
您可以在本地虚拟机或云虚拟机上运行沙箱。Pigsty 提供基于 Vagrant 的本地沙箱(使用 Virtualbox/libvirt 启动本地虚拟机)以及基于 Terraform 的云沙箱(使用云供应商 API 创建虚拟机)。
-
本地沙箱可以在您的 Mac/PC 上免费运行。运行完整的4节点沙箱,您的 Mac/PC 应至少拥有 4C/8G。
-
云沙箱可以轻松创建和共享,单需要一个公有云帐户才行。云上虚拟机可以按需创建/一键销毁,对于快速测试来说非常便宜省事。
此外,Pigsty 还提供了一个 42 节点以上的生产仿真环境沙箱 ha/simu.yml。
Vagrant
Vagrant 可以按照声明式的方式创建本地虚拟机。请查看 Vagrant 模板介绍 以获取详情。
安装
确保您的操作系统中已经安装并可以使用 Vagrant 和 Virtualbox。
如果您使用的是 macOS,您可以使用 homebrew 一键命令安装它们,注意安装 Virtualbox 后需要重启系统。
如果你用的是 Linux,可以使用 virtualbox,也可以考虑使用 KVM: vagrant-libvirt。
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
brew install vagrant virtualbox ansible # 在 MacOS 中可以轻松一键安装,但只有 x86_64 Intel 芯片的可以
配置
vagarnt/Vagranfile 是一个 Ruby 脚本文件,用来描述 Vagrant 要创建的虚拟机节点。Pigsty 提供了一些默认的配置模板:
| 模板 | 快捷方式 | 规格 | 注释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| meta.rb | v1 |
4C8G x 1 | 单一 Meta 节点 |
| dual.rb | v2 |
2C4G x 2 | 双节点测试环境 |
| trio.rb | v3 |
2C4G x 3 | 三节点测试环境 |
| full.rb | v4 |
2C4G + 1C2G x 3 | 完整的 4 节点沙盒示例 |
| minio.rb | vm |
2C4G x 3 + Disk | 3-节点 MinIO/etcd 测试环境 |
| simu.rb | vs |
2C4G x 42+ | 生产模拟仿真环境 |
| pro.rb | vp |
2C4G x 3 | 专业版测试环境 |
| rpm.rb | vr |
2C4G x 3 | RPM 构建测试环境 |
| deb.rb | vd |
2C4G x 3 | Debian 构建测试环境 |
| oss.rb | vo |
2C4G x 3 | OSS 相关测试环境 |
| old.rb | vx |
2C4G x 3 | 旧版本兼容测试环境 |
| all.rb | va |
2C4G x 10+ | 全操作系统版本测试环境 |
| deci.rb | vi |
2C4G x 10+ | Deci 测试环境 |
每个规格文件包含一个描述虚拟机节点的 Specs 变量。例如,full.rb 包含4节点沙盒规格的描述:
Specs = [
{ "name" => "meta" , "ip" => "10.10.10.10" , "cpu" => "2" , "mem" => "4096" , "image" => "bento/rockylinux-9" },
{ "name" => "node-1" , "ip" => "10.10.10.11" , "cpu" => "1" , "mem" => "2048" , "image" => "bento/rockylinux-9" },
{ "name" => "node-2" , "ip" => "10.10.10.12" , "cpu" => "1" , "mem" => "2048" , "image" => "bento/rockylinux-9" },
{ "name" => "node-3" , "ip" => "10.10.10.13" , "cpu" => "1" , "mem" => "2048" , "image" => "bento/rockylinux-9" },
]
您可以使用 vagrant/config 脚本切换 Vagrant 配置文件,它会根据规格以及虚拟机软件类型,渲染生成最终的 Vagrantfile。
cd ~/pigsty
vagrant/config <spec>
vagrant/config meta # 单节点 Meta 环境 | 别名:`make v1`
vagrant/config dual # 双节点测试环境 | 别名:`make v2`
vagrant/config trio # 三节点测试环境 | 别名:`make v3`
vagrant/config full # 4 节点沙箱环境 | 别名:`make v4`
vagrant/config minio # 3 节点 MinIO 环境
vagrant/config simu # 生产模拟仿真环境 | 别名:`make vs`
vagrant/config pro # 专业版测试环境 | 别名:`make vp`
vagrant/config rpm # RPM 构建环境
vagrant/config deb # Debian 构建环境
虚拟机管理
当您使用 vagrant/Vagrantfile 描述了所需的虚拟机后,你可以使用vagrant up命令创建这些虚拟机。
Pigsty 模板默认会使用你的 ~/.ssh/id_rsa[.pub] 作为这些虚拟机的默认ssh凭证。
在开始之前,请确保你有一个有效的ssh密钥对,你可以通过以下方式生成一对:ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 2048
此外,还有一些 makefile 快捷方式包装了 vagrant 命令,你可以使用它们来管理虚拟机。
make # 等于 make start
make new # 销毁现有虚拟机,根据规格创建新的
make ssh # 将 SSH 配置写入到 ~/.ssh/ 中 (新虚拟机拉起后必须完成这一步)
make dns # 将 虚拟机 DNS 记录写入到 /etc/hosts 中 (如果想使用名称访问虚拟机)
make start # 等于先执行 up ,再执行 ssh
make up # 根据配置拉起虚拟机,或启动现有虚拟机
make halt # 关停现有虚拟机 (down,dw)
make clean # 销毁现有虚拟机 (clean/del/destroy)
make status # 显示虚拟机状态 (st)
make pause # 暂停虚拟机运行 (suspend,pause)
make resume # 恢复虚拟机运行 (resume)
make nuke # 使用 virsh 销毁所有虚拟机 (仅libvirt可用)
快捷方式
你可以使用以下的 Makefile 快捷方式使用 vagrant 拉起虚拟机环境。
make meta # 单个元节点
make dual # 双节点测试环境
make trio # 三节点测试环境
make full # 4 节点沙箱环境
make minio # 3 节点 MinIO 测试环境
make simu # 生产模拟仿真环境
make pro # 专业版测试环境
make rpm # RPM 构建环境
make deb # Debian 构建环境
make meta install # 进行完整的单机安装
make full install # 进行 4 节点沙箱安装
make simu install # 进行生产模拟仿真环境安装
...
Terraform
Terraform是一个开源的实践“基础设施即代码”的工具:描述你想要的云资源,然后一键创建它们。
Pigsty 提供了 AWS,阿里云,腾讯云的 Terraform 模板,您可以使用它们在云上一键创建虚拟机。
在 MacOS 上,Terraform 可以使用 homebrew 一键安装:brew install terraform。你需要创建一个云帐户,获取 AccessKey 和 AccessSecret 凭证来继续下面的操作。
terraform/目录包含两个示例模板:一个 AWS 模板,一个阿里云模板,你可以按需调整它们,或者作为其他云厂商配置文件的参考,让我们用阿里云为例:
cd terraform # 进入 Terraform 模板目录
cp spec/alicloud.tf terraform.tf # 使用 阿里云 Terraform 模板
在执行 terraform apply 拉起虚拟机之前,你要执行一次 terraform init 安装相应云厂商的插件。
terraform init # 安装 terraform 云供应商插件:例如默认的 aliyun 插件 (第一次使用时安装即可)
terraform apply # 生成执行计划,显示会创建的云资源:虚拟机,网络,安全组,等等等等……
运行 apply 子命令并按提示回答 yes 后,Terraform 将为你创建虚拟机以及其他云资源(网络,安全组,以及其他各种玩意)。
执行结束时,管理员节点的IP地址将被打印出来,你可以登录并开始完成 Pigsty 本身的安装