参考信息
1 - OS兼容性
概述
Pigsty 建议使用 Linux 内核,amd64 架构的节点,使用 RockyLinux 9.5, Debian 12.10, Ubuntu 22.04.5 操作系统。
内核架构兼容性:Linux 内核,amd64/arm64 架构(x86_64/aarch64)
EL发行版支持: EL8,EL9 ;(RHEL, Rocky, CentOS, Alma, Oracle, Anolis,…)
Debian系发行版支持:Ubuntu 24.04 noble, 22.04 jammy, Debian 12 bookworm;
| Code | Distro | x86_64 |
PG17 | PG16 | PG15 | PG14 | PG13 | Arm64 |
PG17 | PG16 | PG15 | PG14 | PG13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EL9 | RHEL 9 / Rocky9 / Alma9 | el9.x86_64 |
el9.arm64 |
||||||||||
| D12 | Debian 12 (bookworm) | d12.x86_64 |
d12.arm64 |
||||||||||
| U22 | Ubuntu 22.04 (jammy) | u22.x86_64 |
u22.arm64 |
||||||||||
| EL8 | RHEL 8 / Rocky8 / Alma8 / Anolis8 | el8.x86_64 |
el8.arm64 |
||||||||||
| U24 | Ubuntu 24.04 (noble) | u24.x86_64 |
u24.arm64 |
||||||||||
| D11 | Debian 11 (bullseye) | d12.x86_64 |
d11.arm64 |
||||||||||
| U20 | Ubuntu 20.04 (focal) | d12.x86_64 |
u20.arm64 |
||||||||||
| EL7 | RHEL7 / CentOS7 | d12.x86_64 |
el7.arm64 |
= 第一类支持, = 第二类支持, = 第三类支持
Pigsty 不使用任何虚拟化容器化技术,直接运行于裸操作系统上。EL 系与 Debian 系的软件包名有显著差异,默认可用的 PostgreSQL 扩展插件 也会略有不同。
如果您有对兼容性的高级需求,例如使用特定操作系统发行版大小版本,支持特定版本的 PostgreSQL,我们亦提供专业的 服务支持 选项( 与 )。
内核架构兼容性
Pigsty 目前支持 Linux 内核,x86_64 / amd64 芯片架构。
MacOS 与 Windows 操作系统可以通过 Linux 虚拟机/容器的方式安装 Pigsty。
我们提供了 Vagrant 本地沙箱支持,可以在其他操作系统上使用 Vagrant 和 Virtualbox / Libvirtd / VMWare 等虚拟化软件一键拉起 Pigsty 所需的部署环境。您也可以使用 Terraform 在云端环境中一键申请部署 Pigsty 所需的资源。
EL系发行版支持
EL 系操作系统是 Pigsty 的首要支持目标,包括 Red Hat Enterprise Linux,RockyLinux,CentOS,AlmaLinux,OracleLinux, Anolis 等兼容发行版。
Pigsty 支持最近两个大版本: EL9,EL8
- EL9: RHEL,RockyLinux,AlmaLinux ( 推荐使用 Rocky 9.4+)
- EL8: RHEL,RockyLinux,AlmaLinux,Anolis(推荐使用 Rocky 8.10)
- EL7: RHEL,CentOS 7.9 (推荐使用 CentOS 7.9,已在开源版本中弃用!)
| 代码 | 发行版 | 小版本 | PG17 | PG16 | PG15 | PG14 | PG13 | 局限性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHEL 9 / Rocky9 / Alma9 | 9.4 | EL系标准功能集 | ||||||
| RHEL 8 / Rocky8 / Alma8 / Anolis8 | 8.10 | 缺少 pljava, pg_duckdb 等扩展 |
||||||
| RHEL7 / CentOS7 | 7.9 | EOL,PG16/17, 大部分三方扩展不可用 |
建议使用 RockyLinux 9.4
Rocky 9.4+ 在系统可靠性/稳定性与软件版本的新颖性/齐全性上取得了良好的平衡,建议 EL 系用户默认使用此系统版本。EL7 弃用通知
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 已经于 2024年6月停止维护,同时 PGDG 也不再为 PostgreSQL 16 提供 EL7 二进制包支持。
Pigsty 专业版订阅 中提供针对 EL7 操作系统的扩展支持。
Debian系发行版支持
Pigsty 支持 Ubuntu / Debian 系操作系统及其兼容发行版,目前支持
- D12: Debian 12 bookworm(推荐使用 12.7)
- U24: Ubuntu 24.04 jammy(推荐使用 24.04.1 LTS)
- U22: Ubuntu 22.04 jammy(推荐使用 22.04.5 LTS)
U20: Ubuntu 20.04 focal(推荐使用 20.04.6 LTS,已弃用支持) D11: Debian 11 bullseye(推荐使用 11.11,已弃用支持)
| 代码 | Debian系发行版 | 小版本 | PG17 | PG16 | PG15 | PG14 | PG13 | PG12 | 局限性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Debian 12 (bookworm) | 12.7 | Debian标准功能集 | |||||||
| Ubuntu 22.04 (jammy) | 22.04.5 | Ubuntu标准功能集 | |||||||
| Ubuntu 24.04 (noble) | 24.04.1 | 少部分扩展包缺失 | |||||||
| Debian 11 (bullseye) | 11.8 | 已弃用支持 | |||||||
| Ubuntu 20.04 (focal) | 20.04.6 | 已弃用支持 |
建议使用 Debian 12.7 / Ubuntu 22.04.5 LTS
Debian 12 与 Ubuntu 22.04 在系统可靠性/稳定性与软件版本的新颖性/齐全性上取得了良好的平衡。
建议用户默认选择 Debian,有机器学习,桌面等需求则选择 Ubuntu 22.04。
Ubuntu 20.04 / Debian 11 弃用通知
Debian 11 已经于 2024-07 进入 EOL,Ubuntu 20.04 将于 2025-04 进入 EOL。
Pigsty 将不再针对 Debian 11 / Ubuntu 20.04 提供新功能支持与扩展插件打包服务。
Pigsty 专业版订阅 中提供针对 Debian 11 / Ubuntu 20.04 两个过保操作系统大版本的扩展支持。
Vagrant 镜像参考
当您使用云服务器部署 Pigsty 时,可以考虑在 Vagrant 中使用以下操作系统镜像,这也是 Pigsty 开发测试构建使用的镜像。
generic/centos7: CentOS 7.9generic/rocky8: Rocky 8.9generic/rocky9: Rocky 9.5generic/debian11: Debian 11.11generic/debian12: Debian 12.7generic/ubuntu2004: Ubuntu 20.04.6generic/ubuntu2204: Ubuntu 22.04.5bento/ubuntu-24.04: Ubuntu 24.04.1
Terraform 镜像参考
当您使用云服务器部署 Pigsty 时,可以考虑在 Terraform 中使用以下操作系统基础镜像,以阿里云为例:
- CentOS 7.9 :
centos_7_9_x64_20G_alibase_20240628.vhd - Rocky 8.10 :
rockylinux_8_10_x64_20G_alibase_20240923.vhd - Rocky 9.4 :
rockylinux_9_4_x64_20G_alibase_20240925.vhd - Ubuntu 20.04 :
ubuntu_20_04_x64_20G_alibase_20240925.vhd - Ubuntu 22.04 :
ubuntu_22_04_x64_20G_alibase_20240926.vhd - Ubuntu 24.04 :
ubuntu_24_04_x64_20G_alibase_20240923.vhd - Debian 11.11 :
debian_11_11_x64_20G_alibase_20240923.vhd - Debian 12.7 :
debian_12_7_x64_20G_alibase_20240927.vhd - Anolis 8.8 :
anolisos_8_9_x64_20G_rhck_alibase_20240724.vhd
参考阅读
2 - 参数列表
请参考各个功能模块的参数列表:
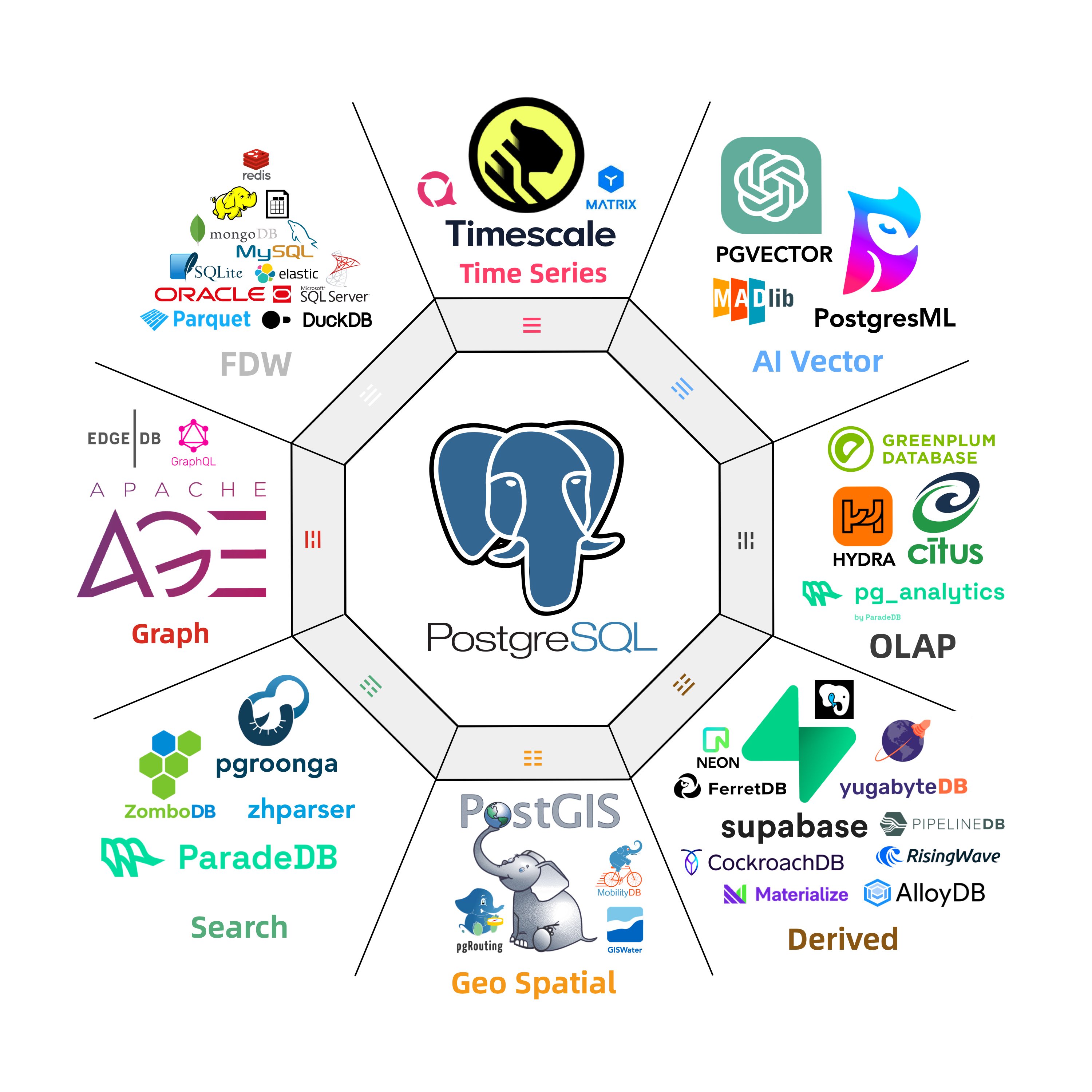
3 - 扩展列表
Pigsty 中总共有 421 个可用扩展,其中 EL 可用 RPM扩展 334 个,Debian/Ubuntu 可用 DEB扩展 326 个。 其中包括 PostgreSQL 自带的 70 个 Contrib扩展。
4 - 文件结构
Pigsty FHS
Pigsty 的主目录默认放置于于 ~/pigsty,该目录下的文件结构如下所示:
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# pigsty
# ^-----@app # 额外的示例应用资源
# ^-----@bin # bin 脚本
# ^-----@docs # 文档(可docsify化)
# ^-----@files # ansible 文件资源
# ^-----@pigsty # pigsty 配置模板文件
# ^-----@prometheus # prometheus 规则定义
# ^-----@grafana # grafana 仪表盘
# ^-----@postgres # /pg/bin/ 脚本
# ^-----@migration # pgsql 迁移任务定义
# ^-----@pki # 自签名 CA 和证书
# ^-----@roles # ansible 剧本实现
# ^-----@templates # ansible 模板文件
# ^-----@vagrant # Vagrant 沙箱虚拟机定义模板
# ^-----@terraform # Terraform 云虚拟机申请模板
# ^-----configure # 配置向导脚本
# ^-----ansible.cfg # ansible 默认配置文件
# ^-----pigsty.yml # pigsty 默认配置文件
# ^-----*.yml # ansible 剧本
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# /etc/pigsty/
# ^-----@targets # 基于文件的服务发现目标定义
# ^-----@dashboards # grafana 监控面板
# ^-----@datasources # grafana 数据源
# ^-----@playbooks # ansible 剧本
# ^-----@pgadmin # pgadmin 服务器列表与密码
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CA FHS
Pigsty 的自签名 CA 位于 Pigsty 主目录下的 files/pki/。
你必须妥善保管 CA 的密钥文件:files/pki/ca/ca.key,该密钥是在 install.yml 或 infra.yml 的 ca 角色负责生成的。
# pigsty/files/pki
# ^-----@ca # 自签名 CA 密钥和证书
# ^-----@ca.key # 非常重要:保守其秘密
# ^-----@ca.crt # 非常重要:在所有地方都受信任
# ^-----@csr # 签名请求 csr
# ^-----@misc # 杂项证书,已签发证书
# ^-----@etcd # etcd 服务器证书
# ^-----@minio # minio 服务器证书
# ^-----@nginx # nginx SSL 证书
# ^-----@infra # infra 客户端证书
# ^-----@pgsql # pgsql 服务器证书
# ^-----@mongo # mongodb/ferretdb 服务器证书
# ^-----@mysql # mysql 服务器证书(占位符)
被 Pigsty 所管理的节点将安装以下证书文件:
/etc/pki/ca.crt # 所有节点都添加的根证书
/etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/ca.crt # 软链接到系统受信任的锚点
所有 infra 节点都会有以下证书:
/etc/pki/infra.crt # infra 节点证书
/etc/pki/infra.key # infra 节点密钥
当您的管理节点出现故障时,files/pki 目录与 pigsty.yml 文件应当在备份的管理节点上可用。你可以用 rsync 做到这一点。
# run on meta-1, rsync to meta2
cd ~/pigsty;
rsync -avz ./ meta-2:~/pigsty
NODE FHS
节点的数据目录由参数 node_data 指定,默认为 /data,由 root 用户持有,权限为 0777。
每个组件的默认数据目录都位于这个数据库目录下,如下所示:
/data
# ^-----@postgres # postgres 数据库目录
# ^-----@backups # postgres 备份数据目录(没有专用备份盘时)
# ^-----@redis # redis 数据目录(多实例共用)
# ^-----@minio # minio 数据目录(单机单盘模式)
# ^-----@etcd # etcd 主数据目录
# ^-----@prometheus # prometheus 监控时序数据目录
# ^-----@loki # Loki 日志数据目录
# ^-----@docker # Docker数据目录
# ^-----@... # 其他组件的数据目录
Prometheus FHS
Prometheus 的主配置文件则位于 roles/infra/templates/prometheus/prometheus.yml.j2 ,并渲染至所有基础设施节点的 /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml。
Prometheus 相关的脚本与规则定义放置于 pigsty 主目录下的 files/prometheus/ 目录,会被拷贝至所有基础设施节点的 /etc/prometheus/ 下。
# /etc/prometheus/
# ^-----prometheus.yml # Prometheus 主配置文件
# ^-----@bin # 工具脚本:检查配置,显示状态,重载配置,重建集群
# ^-----@rules # 记录和报警规则定义
# ^-----agent.yml # agnet 规则和报警
# ^-----infra.yml # infra 规则和报警
# ^-----etcd.yml # etcd 规则和报警
# ^-----node.yml # node 规则和报警
# ^-----pgsql.yml # pgsql 规则和报警
# ^-----redis.yml # redis 规则和报警
# ^-----minio.yml # minio 规则和报警
# ^-----mysql.yml # mysql 规则和报警(占位)
# ^-----@targets # 基于文件的服务发现目标定义
# ^-----@infra # infra 静态目标定义
# ^-----@node # node 静态目标定义
# ^-----@pgsql # pgsql 静态目标定义
# ^-----@pgrds # pgsql 远程RDS目标
# ^-----@redis # redis 静态目标定义
# ^-----@minio # minio 静态目标定义
# ^-----@mongo # mongo 静态目标定义
# ^-----@mysql # mysql 静态目标定义
# ^-----@etcd # etcd 静态目标定义
# ^-----@ping # ping 静态目标定义
# ^-----@patroni # patroni 静态目标定义 (当patroni启用SSL时使用此目录)
# ^-----@..... # 其他监控目标定义
# /etc/alertmanager.yml # 告警组件主配置文件
# /etc/blackbox.yml # 黑盒探测主配置文件
Postgres FHS
以下参数与PostgreSQL数据库目录结构相关:
- pg_dbsu_home: Postgres 默认用户的家目录,默认为
/var/lib/pgsql - pg_bin_dir: Postgres二进制目录,默认为
/usr/pgsql/bin/ - pg_data:Postgres数据库目录,默认为
/pg/data - pg_fs_main:Postgres主数据盘挂载点,默认为
/data - pg_fs_bkup:Postgres备份盘挂载点,默认为
/data/backups(即主数据盘上的子目录)
#--------------------------------------------------------------#
# 工作假设:
# {{ pg_fs_main }} 主数据目录,默认位置:`/data` [快速SSD]
# {{ pg_fs_bkup }} 备份数据盘,默认位置:`/data/backups` [廉价HDD]
#--------------------------------------------------------------#
# 默认配置:
# pg_fs_main = /data 高速SSD
# pg_fs_bkup = /data/backups 廉价HDD (可选)
#
# /pg -> /data/postgres/pg-test-17 (软链接)
# /pg/data -> /data/postgres/pg-test-17/data
#--------------------------------------------------------------#
- name: create postgresql directories
tags: pg_dir
become: yes
block:
- name: make main and backup data dir
file: path={{ item }} state=directory owner=root mode=0777
with_items:
- "{{ pg_fs_main }}"
- "{{ pg_fs_bkup }}"
# pg_cluster_dir: "{{ pg_fs_main }}/postgres/{{ pg_cluster }}-{{ pg_version }}"
- name: create postgres directories
file: path={{ item }} state=directory owner={{ pg_dbsu }} group=postgres mode=0700
with_items:
- "{{ pg_fs_main }}/postgres"
- "{{ pg_cluster_dir }}"
- "{{ pg_cluster_dir }}/bin"
- "{{ pg_cluster_dir }}/log"
- "{{ pg_cluster_dir }}/tmp"
- "{{ pg_cluster_dir }}/cert"
- "{{ pg_cluster_dir }}/conf"
- "{{ pg_cluster_dir }}/data"
- "{{ pg_cluster_dir }}/meta"
- "{{ pg_cluster_dir }}/stat"
- "{{ pg_cluster_dir }}/spool"
- "{{ pg_cluster_dir }}/change"
- "{{ pg_backup_dir }}/backup"
数据文件结构
# 真实目录
{{ pg_fs_main }} /data # 顶层数据目录,通常为高速SSD挂载点
{{ pg_dir_main }} /data/postgres # 包含所有 Postgres 实例的数据目录(可能有多个实例/不同版本)
{{ pg_cluster_dir }} /data/postgres/pg-test-17 # 包含了 `pg-test` 集群的数据 (大版本是 17)
/data/postgres/pg-test-17/bin # 关于 PostgreSQL 的实用脚本
/data/postgres/pg-test-17/log # 日志:postgres/pgbouncer/patroni/pgbackrest
/data/postgres/pg-test-17/tmp # 临时文件,例如渲染出的 SQL 文件
/data/postgres/pg-test-17/cert # postgres 服务器证书
/data/postgres/pg-test-17/conf # postgres 相关配置文件索引
/data/postgres/pg-test-17/data # postgres 主数据目录
/data/postgres/pg-test-17/meta # postgres 身份信息
/data/postgres/pg-test-17/stat # 统计信息,日志报表,汇总摘要
/data/postgres/pg-test-17/spool # 假脱机目录,pgBackRest 临时存储
/data/postgres/pg-test-17/change # 变更记录
/data/postgres/pg-test-17/backup # 指向备份目录的软链接。
{{ pg_fs_bkup }} /data/backups # 可选的备份盘目录/挂载点
/data/backups/postgres/pg-test-17/backup # 集群备份的实际存储位置
# 软链接
/pg -> /data/postgres/pg-test-17 # pg 根软链接
/pg/data -> /data/postgres/pg-test-17/data # pg 数据目录
/pg/backup -> /var/backups/postgres/pg-test-17/backup # pg 备份目录
二进制文件结构
在 EL 兼容发行版上(使用yum),PostgreSQL 默认安装位置为
/usr/pgsql-${pg_version}/
Pigsty 会创建一个名为 /usr/pgsql 的软连接,指向由 pg_version 参数指定的实际版本,例如
/usr/pgsql -> /usr/pgsql-17
因此,默认的 pg_bin_dir 是 /usr/pgsql/bin/,而该路径会被添加至系统的 PATH 环境变量中,定义文件为:/etc/profile.d/pgsql.sh.
export PATH="/usr/pgsql/bin:/pg/bin:$PATH"
export PGHOME=/usr/pgsql
export PGDATA=/pg/data
在 Ubuntu/Debian 上,PostgreSQL Deb 包的默认安装位置是:
/usr/lib/postgresql/${pg_version}/bin
Pgbouncer FHS
Pgbouncer 使用与 {{ pg_dbsu }} (默认为 postgres) 相同的用户运行,配置文件位于/etc/pgbouncer。
pgbouncer.ini,连接池主配置文件database.txt:定义连接池中的数据库userlist.txt:定义连接池中的用户pgb_hba.conf:定义连接池的访问权限
Redis FHS
Pigsty提供了对Redis部署与监控对基础支持。
Redis二进制使用RPM包或复制二进制的方式安装于/bin/中,包括
redis-server
redis-server
redis-cli
redis-sentinel
redis-check-rdb
redis-check-aof
redis-benchmark
/usr/libexec/redis-shutdown
对于一个名为 redis-test-1-6379 的 Redis 实例,与其相关的资源如下所示:
/usr/lib/systemd/system/redis-test-1-6379.service # 服务 (在Debian系中为/lib/systemd)
/etc/redis/redis-test-1-6379.conf # 配置
/data/redis/redis-test-1-6379 # 数据库目录
/data/redis/redis-test-1-6379/redis-test-1-6379.rdb # RDB文件
/data/redis/redis-test-1-6379/redis-test-1-6379.aof # AOF文件
/var/log/redis/redis-test-1-6379.log # 日志
/var/run/redis/redis-test-1-6379.pid # PID
对于 Ubuntu / Debian 而言,systemd 服务的默认目录不是 /usr/lib/systemd/system/ 而是 /lib/systemd/system/
5 - 同类对比
与 RDS 对比
Pigsty 是使用 AGPLv3 开源的本地优先 RDS 替代,可以部署在您自己的物理机/虚拟机上,也可以部署在云服务器上。
因此,我们选择了全球份额第一的亚马逊云 AWS RDS for PostgreSQL,以及中国市场份额第一的阿里云 RDS for PostgreSQL 作为参照对象。
阿里云 RDS 与 AWS RDS 均为闭源云数据库服务,通过租赁模式,仅在公有云上对外提供,以下对比基于最新的 PostgreSQL 16 主干版本进行,对比截止日期为 2024 年 2 月份。
功能特性
| 指标 | Pigsty | Aliyun RDS | AWS RDS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 大版本支持 | 12 - 17 | 12 - 17 | 12 - 17 |
| 只读从库 | 支持任意数量只读从库 | 备实例不对用户开放 | 备实例不对用户开放 |
| 读写分离 | 支持端口区分读写流量 | 独立收费组件 | 独立收费组件 |
| 快慢分离 | 支持离线 ETL 实例 | 未见相关特性 | 未见相关特性 |
| 异地灾备 | 支持备份集群 | 支持多可用区部署 | 支持多可用区部署 |
| 延迟从库 | 支持延迟实例 | 未见相关特性 | 未见相关特性 |
| 负载均衡 | HAProxy / LVS | 独立收费组件 | 独立收费组件 |
| 连接池 | Pgbouncer | 独立收费组件:RDS | 独立收费组件:RDS Proxy |
| 高可用 | Patroni / etcd | 需高可用版提供支持 | 需高可用版提供支持 |
| 时间点恢复 | pgBackRest / MinIO | 提供备份支持 | 提供备份支持 |
| 指标监控 | Prometheus / Exporter | 免费基础版/收费进阶版 | 免费基础版/收费进阶版 |
| 日志采集 | Loki / Promtail | 基础支持 | 基础支持 |
| 可视化系统 | Grafana / Echarts | 提供基本监控 | 提供基本监控 |
| 告警聚合通知 | AlterManager | 基础支持 | 基础支持 |
重要扩展
这里列出了一些重要扩展,对比基于最新的 PostgreSQL 16 主干版本进行,截止至 2024-02-28
| 扩展名称 | Pigsty RDS / PGDG 官方仓库 | 阿里云 RDS | AWS RDS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 加装扩展 | 自由加装 | 不允许 | 不允许 |
| 地理空间 | PostGIS 3.4.2 | PostGIS 3.3.4 / Ganos 6.1 | PostGIS 3.4.1 |
| 雷达点云 | PG PointCloud 1.2.5 | Ganos PointCloud 6.1 | |
| 向量嵌入 | PGVector 0.6.1 / Svector 0.5.6 | pase 0.0.1 | PGVector 0.6 |
| 机器学习 | PostgresML 2.8.1 | ||
| 时序扩展 | TimescaleDB 2.14.2 | ||
| 水平分布式 | Citus 12.1 | ||
| 列存扩展 | Hydra 1.1.1 | ||
| 全文检索 | pg_bm25 0.5.6 |
||
| 图数据库 | Apache AGE 1.5.0 | ||
| GraphQL | PG GraphQL 1.5.0 | ||
| OLAP | pg_analytics 0.5.6 | ||
| 消息队列 | pgq 3.5.0 | ||
| DuckDB | duckdb_fdw 1.1 | ||
| 模糊分词 | zhparser 1.1 / pg_bigm 1.2 | zhparser 1.0 / pg_jieba | pg_bigm 1.2 |
| CDC抽取 | wal2json 2.5.3 | wal2json 2.5 | |
| 膨胀治理 | pg_repack 1.5.0 | pg_repack 1.4.8 | pg_repack 1.5.0 |
AWS RDS PG 可用扩展
AWS RDS for PostgreSQL 16 可用扩展(已刨除PG自带扩展)
| name | pg16 | pg15 | pg14 | pg13 | pg12 | pg11 | pg10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| amcheck | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | yes | 1 |
| auto_explain | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| autoinc | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | null | null | null |
| bloom | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| bool_plperl | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | null | null | null |
| btree_gin | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.2 |
| btree_gist | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| citext | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.4 |
| cube | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.2 |
| dblink | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| dict_int | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| dict_xsyn | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| earthdistance | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| fuzzystrmatch | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| hstore | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.4 |
| hstore_plperl | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| insert_username | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | null | null | null |
| intagg | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| intarray | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| isn | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| jsonb_plperl | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | null | null |
| lo | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| ltree | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| moddatetime | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | null | null | null |
| old_snapshot | 1 | 1 | 1 | null | null | null | null |
| pageinspect | 1.12 | 1.11 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.6 |
| pg_buffercache | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
| pg_freespacemap | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| pg_prewarm | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| pg_stat_statements | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| pg_trgm | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.3 |
| pg_visibility | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| pg_walinspect | 1.1 | 1 | null | null | null | null | null |
| pgcrypto | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
| pgrowlocks | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| pgstattuple | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| plperl | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| plpgsql | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| pltcl | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| postgres_fdw | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| refint | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | null | null | null |
| seg | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.1 |
| sslinfo | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| tablefunc | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| tcn | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| tsm_system_rows | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.1 |
| tsm_system_time | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.1 |
| unaccent | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| uuid-ossp | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
Aliyun RDS PG 可用扩展
阿里云 RDS for PostgreSQL 16 可用扩展(已刨除PG自带扩展)
| name | pg16 | pg15 | pg14 | pg13 | pg12 | pg11 | pg10 | ali_desc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bloom | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 提供一种基于布鲁姆过滤器的索引访问方法。 |
| btree_gin | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 提供一个为多种数据类型和所有enum类型实现B树等价行为的GIN操作符类示例。 |
| btree_gist | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 提供一个为多种数据类型和所有enum类型实现B树等价行为的GiST操作符类示例。 |
| citext | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 提供一种大小写不敏感的字符串类型。 |
| cube | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 提供一种数据类型来表示多维立方体。 |
| dblink | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 跨库操作表。 |
| dict_int | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 附加全文搜索词典模板的示例。 |
| earthdistance | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 提供两种不同的方法来计算地球表面的大圆距离。 |
| fuzzystrmatch | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 判断字符串之间的相似性和距离。 |
| hstore | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 在单一PostgreSQL值中存储键值对。 |
| intagg | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 提供一个整数聚集器和一个枚举器。 |
| intarray | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 提供一些有用的函数和操作符来操纵不含空值的整数数组。 |
| isn | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 按照一个硬编码的前缀列表对输入进行验证,也被用来在输出时连接号码。 |
| ltree | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 用于表示存储在一个层次树状结构中的数据的标签。 |
| pg_buffercache | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 提供一种方法实时检查共享缓冲区。 |
| pg_freespacemap | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 检查空闲空间映射(FSM)。 |
| pg_prewarm | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 提供一种方便的方法把数据载入到操作系统缓冲区或者PostgreSQL缓冲区。 |
| pg_stat_statements | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 提供一种方法追踪服务器执行的所有SQL语句的执行统计信息。 |
| pg_trgm | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 提供字母数字文本相似度的函数和操作符,以及支持快速搜索相似字符串的索引操作符类。 |
| pgcrypto | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 为PostgreSQL提供了密码函数。 |
| pgrowlocks | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 提供一个函数来显示一个指定表的行锁定信息。 |
| pgstattuple | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 提供多种函数来获得元组层的统计信息。 |
| plperl | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 提供perl过程语言。 |
| plpgsql | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 提供SQL过程语言。 |
| pltcl | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 提供tcl过程语言。 |
| postgres_fdw | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 跨库操作表。 |
| sslinfo | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 提供当前客户端提供的 SSL 证书的有关信息。 |
| tablefunc | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 包括多个返回表的函数。 |
| tsm_system_rows | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 提供表采样方法SYSTEM_ROWS。 |
| tsm_system_time | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 提供了表采样方法SYSTEM_TIME。 |
| unaccent | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 文本搜索字典,它能从词位中移除重音(附加符号)。 |
| uuid-ossp | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 提供函数使用几种标准算法之一产生通用唯一标识符(UUID)。 |
| xml2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 提供XPath查询和XSLT功能。 |
性能对比
| 指标 | Pigsty | Aliyun RDS | AWS RDS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 最佳性能 | PGTPC on NVME SSD 评测 sysbench oltp_rw | RDS PG 性能白皮书 sysbench oltp 场景 每核 QPS 4000 ~ 8000 | |
| 存储规格:最高档容量 | 32TB / NVME SSD | 32 TB / ESSD PL3 | 64 TB / io2 EBS Block Express |
| 存储规格:最高档IOPS | 4K随机读:最大3M,随机写 2000~350K | 4K随机读:最大 1M | 16K随机IOPS: 256K |
| 存储规格:最高档延迟 | 4K随机读:75µs,随机写 15µs | 4K随机读:200µs | 500µs / 推断为16K随机IO |
| 存储规格:最高档可靠性 | UBER < 1e-18,折合18个9 MTBF: 200万小时 5DWPD,持续三年 | 可靠性 9个9, 合 UBER 1e-9 存储与数据可靠性 | 持久性:99.999%,5个9 (0.001% 年故障率) io2 说明 |
| 存储规格:最高档成本 | 31.5 ¥/TB·月 ( 5年质保均摊 / 3.2T / 企业级 / MLC ) | 3200¥/TB·月 (原价 6400¥,包月4000¥) 3年预付整体打5折才有此价格 | 1900 ¥/TB·月 使用最大规格 65536GB / 256K IOPS 最大优惠 |
可观测性
Pigsty 提供了近 3000 类监控指标,提供了 50+ 监控面板,覆盖了数据库监控、主机监控、连接池监控、负载均衡监控等方方面面,为用户提供无与伦比的可观测性体验。

Pigsty 提供了 638 与 PostgreSQL 有关的监控指标,而 AWS RDS 只有 99 个,阿里云 RDS 更是只有个位数指标:

此外,也有一些项目提供了监控 PostgreSQL 的能力,但都相对比较简单初级:
- pgwatch: 123 类指标
- pgmonitor : 156 类指标
- datadog : 69 类指标
- pgDash
- ClusterControl
- pganalyze
- Aliyun RDS : 8 类指标
- AWS RDS : 99 类指标
- Azure RDS
可维护性
| 指标 | Pigsty | Aliyun RDS | AWS RDS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 系统易用性 | 简单 | 简单 | 简单 |
| 配置管理 | 配置文件 / CMDB 基于 Ansible Inventory | 可使用 Terraform | 可使用 Terraform |
| 变更方式 | 幂等剧本 基于 Ansible Playbook | 控制台点击操作 | 控制台点击操作 |
| 参数调优 | 自动根据节点适配 四种预置模板 OLTP, OLAP, TINY, CRIT | ||
| Infra as Code | 原生支持 | 可使用 Terraform | 可使用 Terraform |
| 可定制参数点 | Pigsty Parameters 283 个 | ||
| 服务与支持 | 提供商业订阅支持兜底 | 提供售后工单支持 | 提供售后工单支持 |
| 无互联网部署 | 可离线安装部署 | N/A | N/A |
| 数据库迁移 | 提供从现有v10+ PG实例基于逻辑复制不停机迁移至Pigsty托管实例的剧本 | 提供上云辅助迁移 Aliyun RDS 数据同步 |
成本
经验上看,软硬件资源的部分 RDS 单位成本是自建的 5 ~ 15 倍,租售比通常在一个月。详情请参考 成本分析。
| 要素 | 指标 | Pigsty | Aliyun RDS | AWS RDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 成本 | 软件授权/服务费用 | 免费,硬件约 20 - 40 ¥/核·月 | 200 ~ 400 ¥/核·月 | 400 ~ 1300 ¥/核·月 |
| 服务支持费用 | 服务约 100 ¥/ 核·月 | 包含在 RDS 成本中 |
其他本地数据库管控软件
一些提供管理 PostgreSQL 能力的软件与供应商
- Aiven: 闭源商业云托管方案
- Percona: 商业咨询,简易PG发行版
- ClusterControl:商业数据库管控软件
其他 Kubernetes Operator
Pigsty 拒绝在生产环境中使用 Kubernetes 管理数据库,因此与这些方案在生态位上存在差异。
- PGO
- StackGres
- CloudNativePG
- TemboOperator
- PostgresOperator
- PerconaOperator
- Kubegres
- KubeDB
- KubeBlocks
更多信息请参阅:
6 - 成本参考
总体概览
| EC2 | 核·月 | RDS | 核·月 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DHH 自建核月价格(192C 384G) | 25.32 | 初级开源数据库DBA参考工资 | 15K/人·月 |
| IDC自建机房(独占物理机: 64C384G) | 19.53 | 中级开源数据库DBA参考工资 | 30K/人·月 |
| IDC自建机房(容器,超卖500%) | 7 | 高级开源数据库DBA参考工资 | 60K/人·月 |
| UCloud 弹性虚拟机(8C16G,有超卖) | 25 | ORACLE 数据库授权 | 10000 |
| 阿里云 弹性服务器 2x内存(独占无超卖) | 107 | 阿里云 RDS PG 2x内存(独占) | 260 |
| 阿里云 弹性服务器 4x内存(独占无超卖) | 138 | 阿里云 RDS PG 4x内存(独占) | 320 |
| 阿里云 弹性服务器 8x内存(独占无超卖) | 180 | 阿里云 RDS PG 8x内存(独占) | 410 |
| AWS C5D.METAL 96C 200G (按月无预付) | 100 | AWS RDS PostgreSQL db.T2 (2x) | 440 |
| AWS C5D.METAL 96C 200G (预付三年) | 80 | AWS RDS PostgreSQL db.M5 (4x) | 611 |
| AWS C7A.METAL 192C 384G (预付三年) | 104.8 | AWS RDS PostgreSQL db.R6G (8x) | 786 |
RDS成本参考
| 付费模式 | 价格 | 折合每年(万¥) |
|---|---|---|
| IDC自建(单物理机) | ¥7.5w / 5年 | 1.5 |
| IDC自建(2~3台组HA) | ¥15w / 5年 | 3.0 ~ 4.5 |
| 阿里云 RDS 按需 | ¥87.36/时 | 76.5 |
| 阿里云 RDS 月付(基准) | ¥4.2w / 月 | 50 |
| 阿里云 RDS 年付(85折) | ¥425095 / 年 | 42.5 |
| 阿里云 RDS 3年付(5折) | ¥750168 / 3年 | 25 |
| AWS 按需 | $25,817 / 月 | 217 |
| AWS 1年不预付 | $22,827 / 月 | 191.7 |
| AWS 3年全预付 | 12w$ + 17.5k$/月 | 175 |
| AWS 中国/宁夏按需 | ¥197,489 / 月 | 237 |
| AWS 中国/宁夏1年不预付 | ¥143,176 / 月 | 171 |
| AWS 中国/宁夏3年全预付 | ¥647k + 116k/月 | 160.6 |
我们可以对比一下自建与云数据库的成本差异:
| 方式 | 折合每年(万元) |
|---|---|
| IDC托管服务器 64C / 384G / 3.2TB NVME SSD 660K IOPS (2~3台) | 3.0 ~ 4.5 |
| 阿里云 RDS PG 高可用版 pg.x4m.8xlarge.2c, 64C / 256GB / 3.2TB ESSD PL3 | 25 ~ 50 |
| AWS RDS PG 高可用版 db.m5.16xlarge, 64C / 256GB / 3.2TB io1 x 80k IOPS | 160 ~ 217 |
ECS 成本参考
排除 NVMe SSD / ESSD PL3 后的纯算力价格对比
以阿里云为例,纯算力包月模式的价格是自建基准的 5 ~ 7 倍,预付五年的价格是自建的 2 倍
| 付费模式 | 单价(¥/核·月) | 相对于标准价格 | 自建溢价倍率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 按量付费(1.5倍) | ¥ 202 | 160 % | 9.2 ~ 11.2 |
| 包月(标准价格) | ¥ 126 | 100 % | 5.7 ~ 7.0 |
| 预付一年(65折) | ¥ 83.7 | 66 % | 3.8 ~ 4.7 |
| 预付二年(55折) | ¥ 70.6 | 56 % | 3.2 ~ 3.9 |
| 预付三年(44折) | ¥ 55.1 | 44 % | 2.5 ~ 3.1 |
| 预付四年(35折) | ¥ 45 | 35 % | 2.0 ~ 2.5 |
| 预付五年(30折) | ¥ 38.5 | 30 % | 1.8 ~ 2.1 |
| DHH @ 2023 | ¥ 22.0 | ||
| 探探 IDC 自建 | ¥ 18.0 |
含 NVMe SSD / ESSD PL3 情况下的等效价格对比
包含常用规格后的 NVMe SSD 规格之后,纯算力包月模式的价格是自建基准的 11 ~ 14 倍,预付五年的价格是自建的 9 倍左右。
| 付费模式 | 单价(¥/核·月) | + 40GB ESSD PL3 | 自建溢价比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 按量付费(1.5倍) | ¥ 202 | ¥ 362 | 14.3 ~ 18.6 |
| 包月(标准价格) | ¥ 126 | ¥ 286 | 11.3 ~ 14.7 |
| 预付一年(65折) | ¥ 83.7 | ¥ 244 | 9.6 ~ 12.5 |
| 预付二年(55折) | ¥ 70.6 | ¥ 230 | 9.1 ~ 11.8 |
| 预付三年(44折) | ¥ 55.1 | ¥ 215 | 8.5 ~ 11.0 |
| 预付四年(35折) | ¥ 45 | ¥ 205 | 8.1 ~ 10.5 |
| 预付五年(30折) | ¥ 38.5 | ¥ 199 | 7.9 ~ 10.2 |
| DHH @ 2023 | ¥ 25.3 | ||
| 探探 IDC 自建 | ¥ 19.5 |
DHH案例:192核配12.8TB Gen4 SSD (1c:66);探探案例: 64核配3.2T Gen3 MLC SSD (1c:50)。
云上价格每核配比40GB ESSD PL3(1核:4x内存:40x磁盘)计算。
EBS成本参考
| 评估因素 | 本地 PCI-E NVME SSD | Aliyun ESSD PL3 | AWS io2 Block Express |
|---|---|---|---|
| 容量 | 32TB | 32 TB | 64 TB |
| IOPS | 4K随机读:600K ~ 1.1M 4K随机写 200K ~ 350K | 4K随机读:最大 1M | 16K随机IOPS: 256K |
| 延迟 | 4K随机读:75µs 4K随机写:15µs | 4K 随机读: 200µs | 随机IO:500µs 上下文推断为16K |
| 可靠性 | UBER < 1e-18,折合18个9 MTBF: 200万小时 5DWPD,持续三年 | 数据可靠性 9个9 存储与数据可靠性 | 持久性:99.999%,5个9 (0.001% 年故障率) io2 说明 |
| 成本 | **16 ¥/TB·**月 ( 5年均摊 / 3.2T MLC ) 5 年质保,¥3000 零售 | **3200¥/TB·**月 (原价 6400¥,包月4000¥) 3年预付整体打5折才有此价格 | **1900 ¥/TB·**月 使用最大规格 65536GB 256K IOPS 最优惠状态 |
| SLA | 5年质保 出问题直接换新 | Aliyun RDS SLA 可用性 99.99%: 月费 15% 99%: 月费 30% 95%: 月费 100% | Amazon RDS SLA 可用性 99.95%: 月费 15% 99%: 月费 25% 95%: 月费 100% |
S3成本参考
| Date | $/GB·月 | ¥/TB·5年 | HDD ¥/TB | SSD ¥/TB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006.03 | 0.150 | 63000 | 2800 | |
| 2010.11 | 0.140 | 58800 | 1680 | |
| 2012.12 | 0.095 | 39900 | 420 | 15400 |
| 2014.04 | 0.030 | 12600 | 371 | 9051 |
| 2016.12 | 0.023 | 9660 | 245 | 3766 |
| 2023.12 | 0.023 | 9660 | 105 | 280 |
| 其他参考价 | 高性能存储 | 顶配底折价 | 与采购NVMe SSD | 价格参考 |
| S3 Express | 0.160 | 67200 | DHH 12T | 1400 |
| EBS io2 | 0.125 + IOPS | 114000 | Shannon 3.2T | 900 |
下云合集
曾几何时,“上云“近乎成为技术圈的政治正确,整整一代应用开发者的视野被云遮蔽。就让我们用实打实的数据分析与亲身经历,讲清楚公有云租赁模式的价值与陷阱 —— 在这个降本增效的时代中,供您借鉴与参考 —— 请看 《云计算泥石流:合订本》
云基础资源篇
云商业模式篇
下云奥德赛篇
云故障复盘篇
RDS翻车篇
云厂商画像篇
-
互联网技术大师速成班 【转载】
-
门内的国企如何看门外的云厂商【转载】
-
卡在政企客户门口的阿里云【转载】
-
互联网故障背后的草台班子们【转载】
-
云厂商眼中的客户:又穷又闲又缺爱【转载】